Guidelines and standards
Since even the smallest weak spots can contaminate entire production lines, Ganter decided to develop a special series of standard parts that meet the high requirements of the EHEDG and the 3-A Sanitary Standards.
EHEDG
European Hygienic Engineering & Design Group (EHEDG) is a network of experts of machine and component manufacturers, food industry specialists, research institutes and health agencies. The organization was founded in 1989 with the intention of raising awareness on hygiene in food processing and packaging.
EHEDG aims to contribute to the hygienic design in all areas of food production so as to ensure safe manufacturing of foods. EHEDG supports European law and its promotion of hygienic handling, processing, and packaging of foods using hygienic machines and in a hygienic environment (EC Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC, EN 1672-2, and EN ISO 14159 for hygiene requirements).
EHEDG’s mission: “As an expert authority, EHEDG facilitates the safe production of foods by offering expertise in hygienic engineering and design.”
3A
3-A Sanitary Standards, Inc. (3-A SSI) is an independent, not-for-profit corporation in the USA dedicated to advancing hygienic design in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. The 3-A guidelines are intended for the design, manufacture, and cleaning options for daily food auxiliary equipment used in the handling, manufacturing, and packaging of consumable products that have high hygiene requirements. The objective of 3-A SSI is the protection of consumable consumer goods from contamination, the ensuring of automated cleaning of all product surfaces, and simple disassembly for manual cleaning.
FDA
The FOOD AND DRUG ADMINISTRATION (FDA) is a federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States’ executive departments. The FDA is responsible for many things including food safety. The FDA has a positive list of substances that are allowed to come into contact with foods and beverages.
DGUV-Test
DGUV-Test is the testing and certification system of the German Social Accident Insurance Association (DGUV), which consolidates the testing and certification bodies of the various trade associations. The testing and certification bodies within DGUV-Test are conformity assessment bodies for testing and certifying products, specific aspects and processes as well as for auditing and certifying management systems.
Food and packaging testing and certification body within DGUV-Test
This testing and certification body specialized in food is an accredited and notified body headquartered in Mannheim with another testing laboratory in Mainz. The focus of the testing work in the Mannheim testing laboratory lies primarily on packaging and other food-processing machines. Specific aspects, such as hygiene, can also be tested and certified. Tested and certified products are entitled to display the DGUV-Test mark as a quality product. The DGUV-Test mark “Hygiene tested” confirms that the hygiene requirements according to European regulations are complied with. All tests can be carried out in parallel with the development process, which offers an important time advantage for the market introduction of products.
BGN
The Food and Hospitality Trade Association (BGN), headquartered in Mannheim, offers safety-related consulting relating to machines and components. Other services include seminars on a variety of topics in the areas of occupational safety and protection of health. BGN experts are active in these areas of national, European and international standardization and contribute their knowledge and experience in special panels. The resulting standards are then used as a basis for designing and engineering machines. In this way, a primary preventive benefit is achieved since safety and hygiene are integrated by standard.
Product family Hygienic Design
All Standard Parts of the “Hygienic Design” product family are labeled with the HD icon. They combine high surface quality, freedom from dead spaces, non-scooped outer surfaces, and sealed bolting areas. A sealing concept based on FEM calculations ensures reliable contact pressure after installation.
Hygienic Design also means that the time and material needed for regular cleaning is significantly reduced—which also noticeably lowers operating costs.
Whitepaper for food & pharma
The design of systems for areas with critical hygiene requirements always poses great challenges to designers and machine builders. Ganter supplies solutions and ideas for avoiding cost traps.
Principles
In the food industry, medical technology and the pharmaceutical industry, product safety and consumer protection are becoming increasingly important.
Due to their specific properties, standard parts in hygienic design can support the production process in these sensitive areas and facilitate the manufacture of products with a long shelf life, reducing the need for preservative agents.
Less time-consuming cleaning work (up to 25% of the production time), therefore
- more time available for production
- less fresh water consumption
- lower energy consumption
- less cleaning agent required
- less production of waste water
- lower total costs and saving of resources
EN 1672-2:2009 “Food processing machinery”
- Machines must cleanable, i.e. they must be designed and constructed so that dirt can be removed with the recommended cleaning methods.
Machinery directive 2006/42/EC
- Machines must be designed so that
- materials can be easily and fully cleaned before each use and
- no risk of infections or illness is created.
DIN EN ISO 14519:2008-07
- Hygiene requirements for the design of machines
DIN EN 1672-2:2021-05
- Food processing machinery – Basic concepts
Material
- Non-rusting Stainless Steels
- FDA and EU compliant plastics and elastomers
Surfaces
- Surfaces must be able to be cleaned
- Steps due to appliance configurations which are not aligned must be avoided
- Seals must be designed so that no gaps occur
- O-ring grooves must be hygienically designed
- Contact with the product to be manufactured must be ruled out
- Corners should preferably have a radius of 6 mm or more
Design / Geometry
- The interior and exterior areas of all appliances, components or piping must be self-draining or be able to be drained and easy to clean.
- European Hygienic Engineering & Design Group
- Non-profit European consortium of machine and food manufacturers as well their suppliers, research institutes, universities and government health agencies
- Roughly 45 guidelines
- Examination of products and issue of certificates
- Non-profit and independent association in the USA
- Three interest groups: public and governmental health agencies, machine manufacturers and food manufacturers
- Over 70 sanitary standards
- Examination of designs and processes, issue of certificates
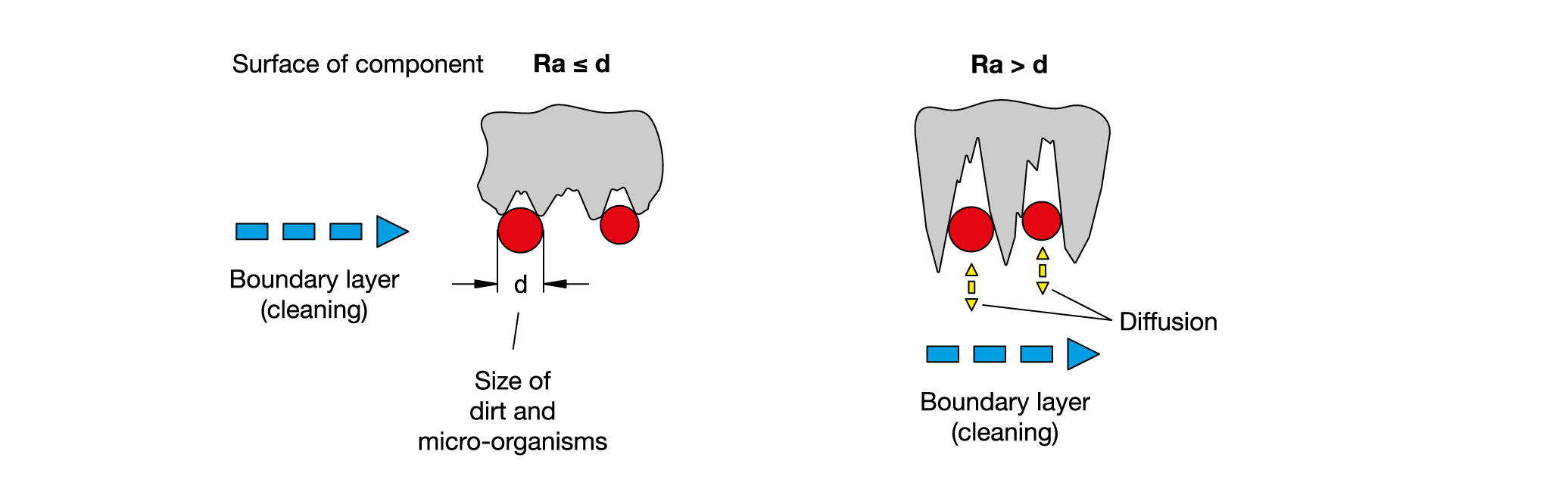
Surface properties and roughness Ra < 0.8 µm
Seals
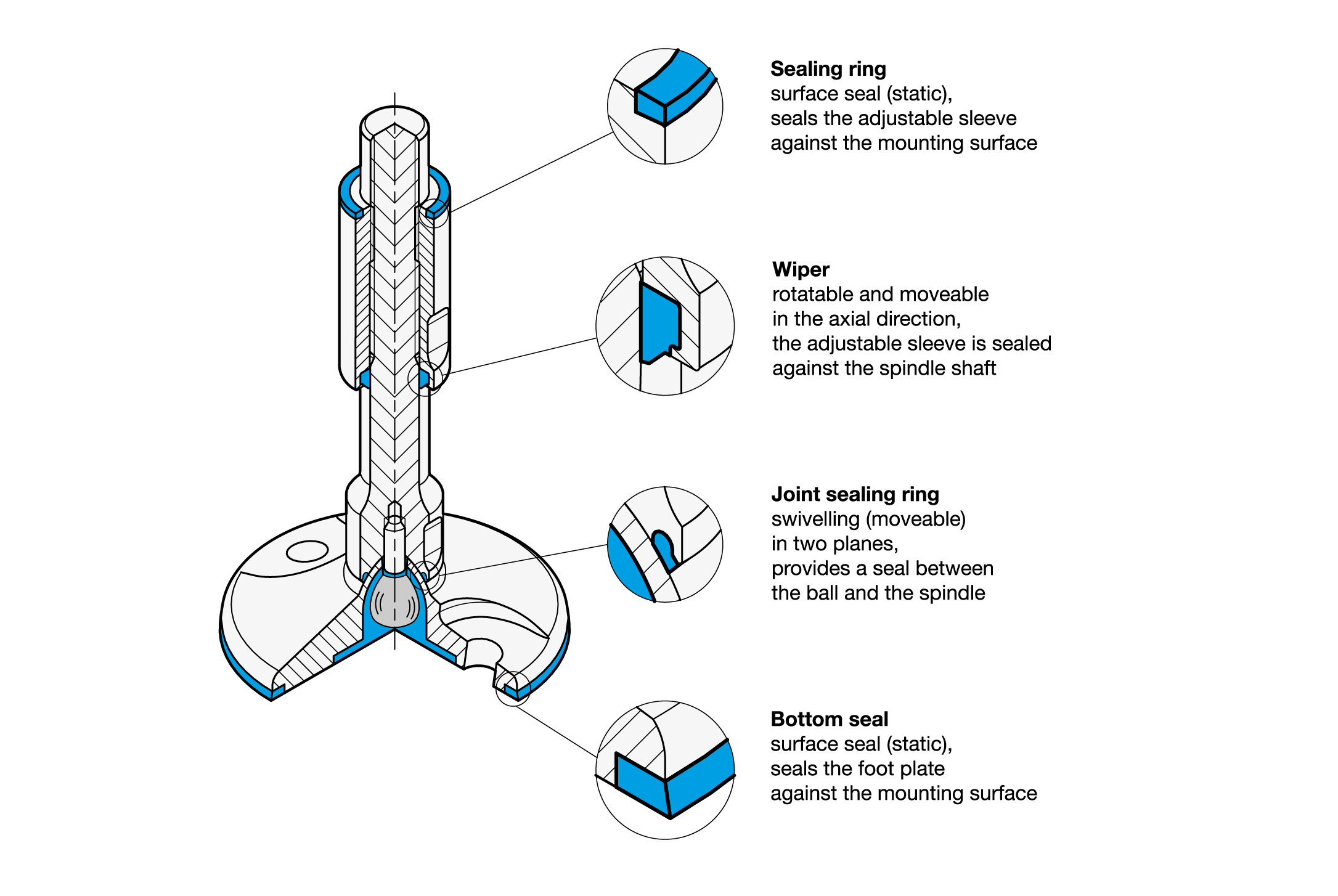
For the standard parts which are listed in Hygienic Design, seals have the central function of protecting dead spaces, gaps and cracks from the penetration of cleaning fluids or product residues.
For this, a defined pre-tension or pressing of the seals and wipers is necessary for a reliable and permanent seal in the installed condition. Within the Hygienic Design product family, seal installation spaces and seal cross sections are calculated and designed with simulation software, so that the necessary surface compression is achieved on installation and the seal material is not subjected to excess pressure.
A fundamental differentiation can be made between static and moving seals:
- During assembly, the static seals in the design example shown here are tightened to the mounting surface at the top (sealing ring) and to the contact surface at the bottom (bottom seal). It should be ensured that all surfaces which make contact with the seal have a surface finish of at least Ra 0.8 µm.
- The moving seals on the adjustment sleeve (wiper) and the ball joint (joint seal) of the foot are designed so that they allow adjustment in both height and angle. With these too, the installation space together with the cross section of the seal ensures a gap-free, pre-tensioned seal.
Depending on the version and the type of use, it may be the case that seals may need to be replaced in case of damage or for preventative maintenance. For this, Ganter supplies the relevant seals as spare parts or offers these under GN 7600 as standard parts for spare parts.
Certified quality
Together with the Fraunhofer Institut, the cleanability of the surface was assessed based on levelling foot GN 20: