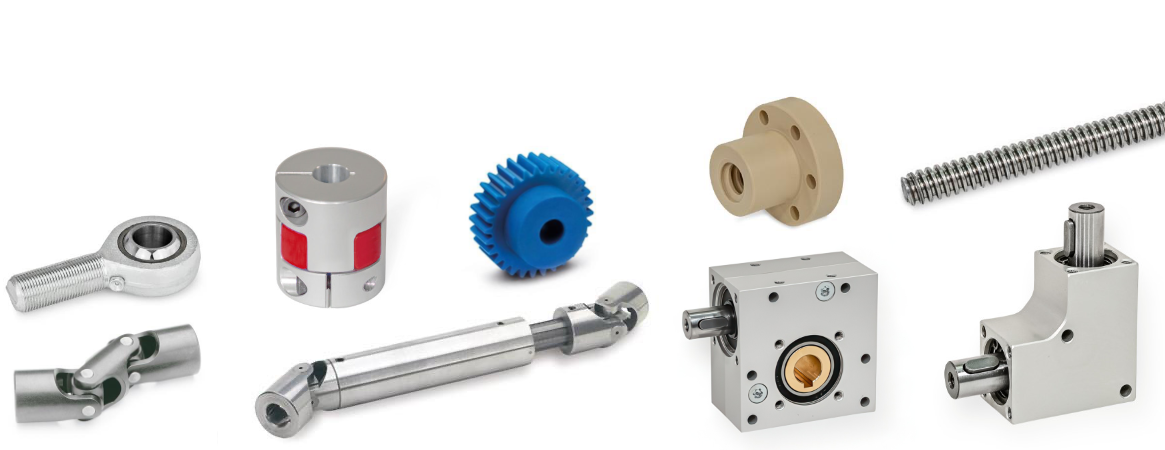
Gear boxes
Bevel gear boxes GN 3971 and worm gear reducers GN 3975 can transmit high torque despite their very compact dimensions. They can readily be used for a multitude of applications and require no maintenance.
Gear boxes from Ganter feature the following advantages:
- Self-lubricated
- Long service life
- Very quiet operation
- Encapsulated housing to prevent the entry of dust
- Low backlash on reversal
- More mounting options
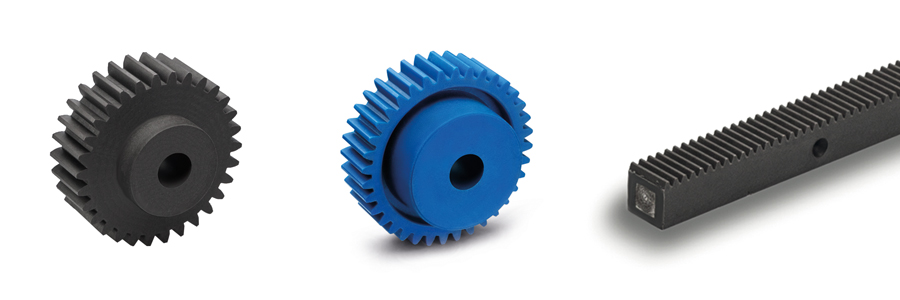
Gears
Gears and racks of polyamide are preferred in mechanisms that must transmit high torques at low speeds. Applications include packaging machines, plants in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries and in food production. The components are combined to convert rotational movements into linear movements or vice versa. Synchronous, symmetrical or even proportional movements can also be easily realized, such as for clamping jaws, grippers or ganged components.

Universal joint shafts
Universal joint shafts transmit rotation and torque from shafts that can be at a changeable angle, offset and distance to each other. A variety of materials are available as well as designs with friction bearings and with needle bearings for higher demands. The length compensation is achieved with a splined shaft, which is inserted into a sliding sleeve.

Couplings
A coupling creates the connection between the drive shaft and the driven shaft in order to transmit rotary motion and torque. For example, they are used to combine the shafts of motors and transmissions into a single drive unit.
Aside from their primary purpose of transmitting torque, couplings also flexibly perform other important tasks:
- Compensating for shaft offsets and misalignments
- Absorbing runout errors and axial motions
- Damping vibrations and shocks
Couplings are used in a very wide range of applications. The spectrum ranges from simple drives to complex control, regulation and measurement applications.

Trapezoidal thread spindles, trapezoidal thread nuts
Quick-fit couplings are used to compensate for a radial offset, such as of a pressure cylinder piston rod relative to the driven component. Depending on the design, even zero backlash compensation of an angled offset is possible.
Show all trapezoidal thread spindles, trapezoidal thread nuts







